Chapter 7 Bankruptcy & Credit Reports
Contents
- Chapter 7 Bankruptcy & Credit Reports
- What is Chapter 7 Bankruptcy?
- How does Chapter 7 Bankruptcy impact your credit score?
- What is a credit report?
- Credit Report vs. Credit Score
- How long does Chapter 7 Bankruptcy stay on your credit report?
- How Chapter 7 Bankruptcy affects your ability to get credit
- Improve Credit Score after Bankruptcy.
- Alternative ways to handle debt
One of the most common types of bankruptcy is Chapter 7 bankruptcy, which involves liquidating assets to pay off creditors. After going through this process, one of the most pressing concerns for most individuals is how long the bankruptcy will stay on their credit report. In this blog post, we will explore the details of Chapter 7 bankruptcy and discuss how long it will impact your credit report. We will look at the different factors that affect your credit score, how to rebuild your credit and provide tips on how to bounce back from bankruptcy. So, if you’re considering filing for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, keep reading to learn more about what to expect.
What is Chapter 7 Bankruptcy?
Chapter 7 bankruptcy is a legal process that allows individuals, partnerships, or businesses to have their debts discharged. It is also known as “liquidation bankruptcy” because the debtor’s non-exempt assets are sold, and the proceeds are used to pay off as much of the debt as possible. Any remaining debt that cannot be paid is discharged, meaning the debtor is no longer legally obligated to pay it.
Chapter 7 bankruptcy is a popular choice for those with a lot of unsecured debt, such as credit card debt or medical bills, who do not have the means to pay them off. However, not everyone is eligible for Chapter 7 bankruptcy. To qualify, the debtor must pass a means test, which compares their income to the median income in their state. If their income is below the median, they may be eligible for Chapter 7 bankruptcy.
Not all debts can be discharged in Chapter 7 bankruptcy. Some debts, such as student loans and tax debts, are not dischargeable. Additionally, the bankruptcy will not discharge any debts incurred after filing.
How does Chapter 7 Bankruptcy impact your credit score?
Filing for Chapter 7 Bankruptcy is a serious financial decision that can have long-lasting impacts. One of the most significant impacts is on your credit score.
Chapter 7 Bankruptcy will stay on your credit report for up to 10 years from the filing date. For a decade, lenders, banks, and other financial institutions can see that you filed for bankruptcy, which may impact your ability to secure credit or loans.
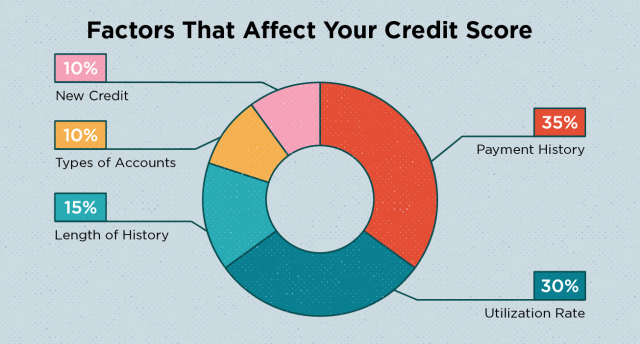
Bankruptcy will lower your credit score significantly, and the exact impact will depend on your credit score before filing. If you had a high credit score before filing for bankruptcy, you could see your score drop by 200-250 points. On the other hand, if your credit score was already low before filing, the impact may be less severe.
It’s important to note that even after the bankruptcy is removed from your credit report after ten years, the effects of the bankruptcy may still linger. Potential lenders may view you as a higher-risk borrower, and you may be subject to higher interest rates or other unfavorable terms.
However, it’s not all doom and gloom. Take steps to rebuild your credit by making timely payments, keeping your credit utilization low, and avoiding high-risk behavior. You can start to rebuild your credit score over time. While bankruptcy may stay on your credit report for a long time, it doesn’t have to define your financial future.
What is a credit report?
Credit reports are used by lenders, landlords, and other businesses to determine an individual’s creditworthiness and ability to repay loans. A credit report is a detailed summary of an individual’s credit history maintained by credit bureaus. It includes information about all credit accounts, such as:
- credit cards
- loans
- mortgages
The report also includes information regarding the individuals:
- payment history
- credit limits
- outstanding balances
Additionally, a credit report includes information about:
- bankruptcies
- foreclosures
- collections
Regularly review your credit report to ensure all the information is accurate and up-to-date. If you have filed for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, it will stay on your credit report for up to 10 years. It may be more difficult to obtain credit or loans during this time, and you may be subject to higher interest rates.
However, it is not impossible to rebuild your credit after bankruptcy. Making timely payments on any remaining debts and practicing responsible financial habits can help improve your credit score.
Credit Report vs. Credit Score
When understanding your credit, there is often some confusion between a credit report and a credit score. While both are important components of monitoring your finances, it’s important to understand the differences between them to make informed decisions about how you manage your money.
Credit Report
A credit report records your financial history, including details about your credit accounts, such as loans and lines of credit. It shows whether or not you have made payments on time and any other relevant information that helps lenders decide whether or not to approve you for credit. Your credit report provides a comprehensive look at your financial past and can be used to determine if you qualify for new loans and lines of credit.
Credit Score
On the other hand, a credit score is a numerical representation of an individual’s creditworthiness. The most common scoring system is called FICO® Score, which ranges from 300-850, with higher numbers indicating good credit health. When potential lenders review this number, they can get an idea of how likely you are to repay the loan or line of credit they are considering offering you.
How long does Chapter 7 Bankruptcy stay on your credit report?
Chapter 7 bankruptcy is a legal process that can help individuals and businesses eliminate most or all of their unsecured debts. While it can provide a fresh start for those struggling with debt, it can significantly impact their credit report. So, how long does Chapter 7 bankruptcy stay on your credit report?
The answer is that it typically stays on your credit report for 10 years from when the bankruptcy case is filed. This means that any potential lenders or creditors will be able to see the bankruptcy filing on your credit report for the entire 10-year period.
It’s important to understand the impact of bankruptcy on your credit score. Filing for bankruptcy can cause your credit score to drop significantly, and it can take years to rebuild your credit after a bankruptcy filing. However, it’s not all bad news. Many people can rebuild their credit over time by making on-time payments, using credit responsibly, and taking other positive steps to improve their creditworthiness.
How Chapter 7 Bankruptcy affects your ability to get credit
Filing for Chapter 7 bankruptcy can significantly impact your credit score and ability to obtain credit. It can stay on your credit report for up to 10 years, making obtaining a loan, credit card, or mortgage difficult. This is because lenders view bankruptcy as a sign of financial irresponsibility, and they may be hesitant to lend money to someone who has filed for bankruptcy in the past.
If approved for credit after filing for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, you can expect to pay higher interest rates and fees than someone with a good credit score. This can make making ends meet and paying off your debt more difficult. Filing for bankruptcy can also impact your ability to rent an apartment or get a job, as some landlords and employers may view it as a negative mark on your financial record.
It’s important to rebuild your credit after filing for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, such as paying all bills on time, applying for a secured credit card, and keeping credit card balances low. Over time, your credit score will improve, and you’ll be able to qualify for better rates and terms on loans and credit cards.
Improve Credit Score after Bankruptcy.
Filing for Chapter 7 bankruptcy can significantly impact your credit score and ability to obtain credit in the future. However, it’s important to know that you can take steps to rebuild your credit score after filing for bankruptcy.
Here are some tips to improve your credit score after Chapter 7 bankruptcy:
- Check your credit report: First and foremost, check your credit report to ensure all your debts have been discharged. If you find any errors or omissions, you can dispute them with the credit reporting agencies.
- Make timely payments: One of the most important things you can do to rebuild your credit score is to make timely payments on any remaining debts. This includes credit cards, loans, and any other accounts that you have open.
- Use credit responsibly: While it may be tempting to avoid credit altogether after filing for bankruptcy, it’s important to use credit responsibly to rebuild your credit score. This means only taking on new credit accounts that you can manage and making regular, on-time payments.
- Consider a secured credit card: If you’re having trouble obtaining credit after Chapter 7 bankruptcy, consider applying for a secured credit card. These cards require a security deposit but can be a good way to rebuild your credit score.
- Seek professional help: If you’re struggling to improve your credit score independently, consider seeking professional help from a credit counseling agency or a financial advisor. They can provide you with personalized advice and guidance on how to rebuild your credit score after bankruptcy.
Alternative ways to handle debt
If you’re struggling with debt but don’t want to file for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, there are alternative ways to handle your debt.
Debt Consolidation
One option is to consider debt consolidation. This involves combining all your debts into one loan with a lower interest rate and more manageable monthly payments. This can be a good option if you have multiple high-interest debts, such as credit cards or personal loans.
Debt Settlement
Another alternative is debt settlement. This involves negotiating with creditors to settle your debts for less than what you owe. This can be a good option if you have significant debt and cannot make monthly payments. However, debt settlement can hurt your credit score, and there are also risks involved, such as being sued by your creditors.
If you’re struggling to make ends meet and are worried about your debt, exploring your options is important before filing for Chapter 7 bankruptcy. Consider speaking with a financial advisor or credit counselor to understand your financial situation and available options. With the right strategy, you can take control of your debt and get back on track financially.




