Informed vs Expressed Consent: Key Differences and Implications
Consent is a fundamental ethical principle of human interaction, allowing individuals to engage in a variety of activities and transactions that would otherwise be considered wrong.
Understanding consent practices is crucial, as recent surveys show up to 25% of adults struggle to distinguish between express and implied consent.

Whether it’s a contractual agreement between an employer and employee, the difference between consensual sex and rape, the parameters for borrowing or selling items, the consent given before receiving medical treatment, or taking part in research studies, consent is essential to guaranteeing the autonomy of all parties involved.
In Chicago, a recent study found that informed consent forms for surgeries led to a 34% increase in patient satisfaction rates.
Lack of informed consent can lead to exploitation and abuse, or even endangerment in certain cases. As such, recognizing the importance of consent and actively communicating it are necessary components of healthy relationships and responsible social behavior.
What is Consent in Legal and Ethical Contexts?
Consent in legal and ethical contexts refers to permission, approval, or agreement to do something or allow something to happen. Some key things to know about consent in law and ethics:
- Legal Consent – Consent is central to contract law, where agreement between parties forms a contractual obligation. It also comes up in criminal law – sexual acts without consent are considered rape/assault.
- Informed Consent – Giving consent requires being fully informed. This applies in medicine, where doctors must disclose risks/benefits, and in research, where participants must understand the study parameters.
- Express vs. Implied Consent – Express consent is explicitly stated approval. Implied consent is signaled through actions/inaction rather than words. Problems can arise when distinguishing implied vs unconsented.
- Capacity – For consent to be valid, the person must have the mental capacity to make the decision. Those deemed incapacitated cannot legally give consent.
- Coercion – Consent must be given freely, without force or coercion invalidating the agreement. This issue often arises in workplace relationships.
- Withdrawing Consent – People have the right to withdraw consent at any time. This is relevant in medical procedures, where patients can halt treatment.
- Age and Power Dynamics – Minors cannot legally consent to most matters. Power imbalances in relationships raise ethical consent concerns.

Overall, consent requires being fully informed, freely given, and continuously affirmed. It’s a complex concept that forms the basis of many laws and ethical codes across different contexts. Ongoing consent should be actively maintained, not assumed.
Differences Between Express and Implied Consent
Express permission or consent is communicated verbally or in writing and serves as an explicit agreement for medical treatment. Implied consent, however, is a form of agreement that is inferred from the patient’s conduct. For instance, if a patient arrives at the emergency room before they become unconscious, they are providing implicit expressed permission for appropriate medical interventions to occur until they regain their awareness.
A lack of consent contributes to approximately 183,000 unethical medical procedures per year (NLB.gov, 2022).
In the case of minors who are unable to give lawful consent, the implied agreement applies. Although healthcare providers must perform life-saving procedures when needed, it can be challenging to prove this form of consent in a legal setting.
Here are some key differences between express and implied consent:
- Expression – Express consent is explicitly stated, either orally or in writing. Implied consent is not directly expressed, but inferred from actions or inaction.
- Clarity – Express consent clearly communicates permission. Implied consent tends to be ambiguous and open to interpretation.
- Specificity – Express consent often identifies the exact activity or treatment being consented to. Implied consent may be vague.
- Documentation – Express consent is usually evidenced in a written agreement. Implied consent often lacks documentation.
- Intent – Express consent directly indicates intent. The intent behind implied consent may be unclear.
- Legal Strength – Express consent provides stronger legal evidence of permission. Implied consent has more legal ambiguity.
- Ongoing Communication – Express consent requires clearly communicating changes. Implied consent assumes static permission.
- Withdrawal – Express consent can be explicitly revoked. Withdrawing implied consent may be disputed.
- Context Matters – Some situations require express consent by law or ethics policies. Implied consent may be insufficient.
Defining Consent
Consent is the concept that a person has a right to say ‘yes’ or ‘no’ to any kind of activity. It is important to recognize that in order for consent to be valid, both parties must give their full, informed, and mutual agreement.
- Consent can never be assumed or taken for granted; it must always be freely given by one party and willingly accepted by the other.
- Consent is not a one-time event; it should be actively sought throughout the duration of an activity.
- Consent can be revoked at any time for any reason, and no explanations are required.
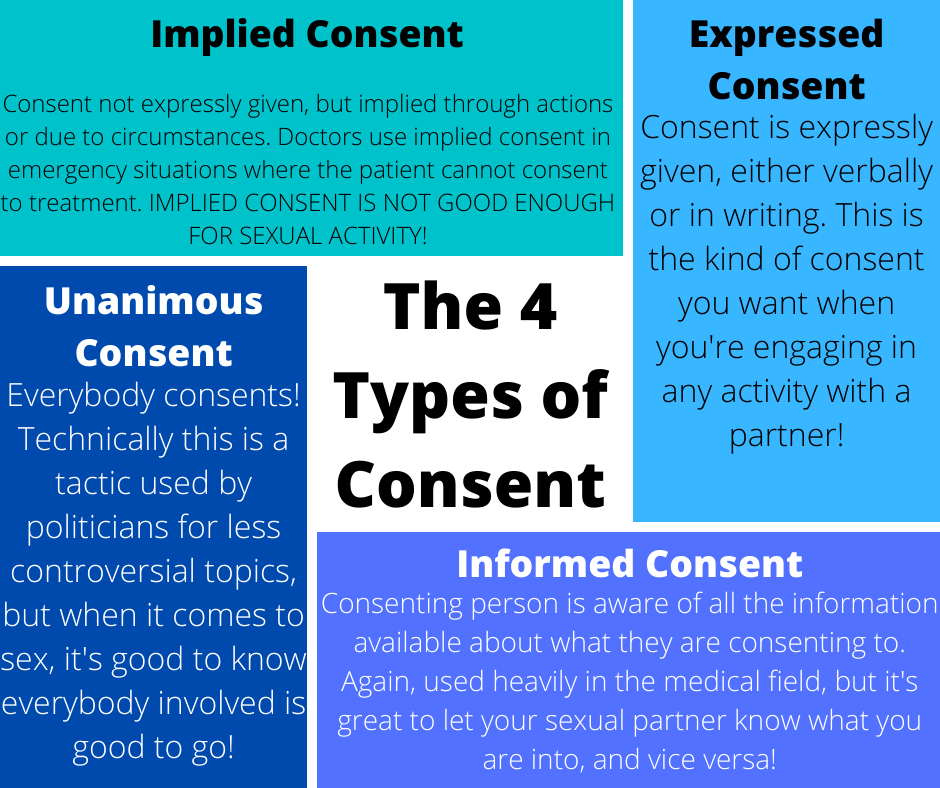
What are the 4 Types of Consent
- Expressed Consent refers to an explicit agreement that is clearly communicated either verbally or in writing. It leaves no room for confusion or misinterpretation. Examples include signed consent forms and verbal confirmation.
- Implied Consent is conveyed by actions rather than words. For example, holding out one’s arm implies consent for a blood pressure reading. Implied consent is assumed but not explicitly stated.
- Informed Consent requires providing information about the benefits, risks, and alternatives so the person fully understands what they are consenting to. Doctors obtain informed consent from patients before medical procedures.
- Unanimous Consent refers to agreement by all members of a group or committee. It requires getting consent from each individual rather than a majority.
Expressed Consent Definition
Express consent is a form of explicit permission that provides undeniable proof that you are aware of, and have given approval for, any proposed course of action or treatment. It is often utilized in medical contexts where both parties must agree and fully understand the implications of the procedures and care in question. Express consent can also be used in other contexts where it is legally required for one party to give authorization to another.
“Express consent” refers to written confirmation of agreement, which can be conveyed electronically and include an electronic signature as defined in section 106(5) of Public Law 106–229. This type of confirmation is essential for the validity of any contract or transaction.
When granting express consent to a doctor or third party, you will usually be asked to sign a document that outlines the details of your agreement. Once signed, it serves as evidence of your full understanding of, and agreement to, the proposed treatment and actions. By providing this express written consent, you are confirming that you had full knowledge and intention when granting permission.
Definitions of Implied Consent
Implied consent is a form of agreement that is inferred from a person’s behavior or the surrounding circumstances. This type of consent can be just as legally binding as express consent, which requires that the parties involved directly and clearly communicate their approval with words.
Clinical trials found that only 52.1% of patients fully understood implied consent for the study. (NIH.gov 2015)
As such, it is important to be knowledgeable about the implications of implied consent in order to avoid potential legal disputes. The most critical factor determining whether implied consent can be established is whether an objectively reasonable individual would conclude that consent was given based on the observed action or lack thereof. If so, the consent is considered valid and enforceable in court.
Implied consent and DUI
Implied consent laws are an important tool in the fight against alcohol-related motor vehicle crashes in the United States. These laws, which impose sanctions on DUI offenders who refuse to submit to chemical BAC tests, serve as a deterrent against such refusals, thus helping to ensure that impaired drivers can be identified and appropriately dealt with by law enforcement.

Laws and Regulations Related to Consent
As a patient, it’s important to be well-informed when giving either express or implied consent for medical treatments and procedures. Express consent is given clearly and directly, such as through written permission or verbal agreement, while implied consent is usually based on signed waivers or a display of willingness.
The HHS outlines strict express parental consent requirements for medical research involving minors under 18 years old. (HHS.gov, 2023)
When providing consent, doctors have a responsibility to ensure you are fully informed of the risks, benefits, and possible side effects involved in any examination or procedure. They should also provide detailed explanations of the procedure before requesting your permission, and adequately answer any questions you may have.
It’s also important for healthcare providers to adhere to a standard of care. This includes properly diagnosing your condition, considering your medical history and current medications, following up with you during your recovery, prescribing appropriate medications in the right dosages, and providing instructions when they discharge you.
If a doctor fails to meet these standards and commits an error that leads to injury or worsened condition, you may be able to hold them responsible through a medical malpractice lawsuit.
What is Express Consent?
Express consent is a clear and unequivocal agreement or permission given explicitly, often in writing or verbally, where the individual provides consent for a specific action or purpose. The elements of express consent typically include:
- Voluntary Agreement: The individual provides consent of their own free will, without coercion, pressure, or manipulation.
- Specificity: Express consent should clearly state the action or purpose for which consent is being given. It should be unambiguous and not open to interpretation.
- Informed Decision: The individual giving consent should have adequate information about the action, its implications, and any potential risks involved. They should understand what they are agreeing to.
- Capacity to Consent: The person providing consent should be of legal age and mental capacity to understand the consequences of their decision. In the case of minors or individuals with diminished capacity, a legal guardian or representative may provide express consent on their behalf.
- Clear Communication: Express consent is typically communicated in writing, orally, or through other clear and easily understood means. It should be evident that the individual has willingly given their agreement.
- Revocable: Express consent can usually be revoked at any time if the individual changes their mind or is no longer comfortable with the action or purpose they initially agreed to.
- Documentation: In many cases, express consent is documented in writing to create a record of the agreement. This can be useful for legal and administrative purposes.
- Signature: In some instances, the consent may require a signature or a mark made by the person providing consent to authenticate their agreement.
Examples of Express Consent in Healthcare
- Medical Procedures: Before performing a medical procedure or surgery, healthcare providers typically obtain express consent from the patient. The patient is informed about the procedure, its risks, benefits, and alternatives. They must sign a consent form to indicate their willingness to undergo the procedure.
- Treatment Plans: In ongoing healthcare, express consent is often required for specific treatments, medications, or therapies. Patients provide explicit consent for these interventions after being informed about their options and potential side effects.
- Emergency Situations: In some urgent medical situations, express consent may not be possible due to the individual’s condition. In such cases, implied consent (based on the assumption that a reasonable person would consent in an emergency) is often relied upon when immediate care is necessary.
Examples of Express Consent in Legal Contracts
- Business Agreements: In the business world, express consent is often obtained in contractual agreements. For instance, when two parties enter into a business contract, they sign a written agreement that outlines the terms and conditions, making their consent explicit.
- Financial Transactions: Banking and financial institutions may require express consent for various transactions, such as loans, investments, or account changes. The customer’s agreement is documented in contracts or terms of service.
Examples of Express Consent in Digital Services
- Privacy Policies: Many online platforms and services require users to provide express consent to their privacy policies, terms of service, and data collection practices. Users often need to click a “I Agree” button or check a box to indicate their consent.
- Email Marketing: Companies often seek express consent to send marketing emails. This consent is obtained through opt-in forms, where individuals voluntarily subscribe to receive promotional messages.
- Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA): Websites and online services directed towards children under 13 must obtain express parental consent before collecting personal information from these children.
What is Implied Consent?
Implied consent is a form of consent that is not expressly given by an individual but is assumed or inferred based on their actions, behavior, or the circumstances of a situation. The elements of implied consent typically include:
- Situational Understanding: Implied consent relies on the assumption that the individual understands the context and purpose of the situation, and their actions suggest they are willing to proceed.
- Reasonable Person Standard: Implied consent often adheres to the “reasonable person” standard, which means that a reasonable person in a similar situation would understand the implications and act in a certain way.
- No Explicit Rejection: Implied consent is typically inferred when there is no explicit rejection or objection from the individual. Their silence or passive participation implies agreement.
- Custom or Common Practice: In some cases, implied consent is based on established customs or common practices. For example, in a medical setting, it may be customary for patients to extend their arm for a blood pressure measurement, implying consent for the procedure.
- Emergency Situations: Implied consent may be assumed in situations where immediate action is necessary to save a person’s life or prevent harm. For example, administering first aid to an unconscious accident victim is often based on implied consent.
- Previous Behavior: Previous behavior or patterns of interaction can also be considered when determining implied consent. For example, an individual’s history of routinely accepting a certain type of service or intervention can imply their consent to it in the future.
- Cultural and Social Norms: Cultural and social norms may influence the interpretation of implied consent. What is considered acceptable behavior can vary from one culture to another.
- Scope and Limits: Implied consent is typically limited in scope. It is presumed only for actions that are reasonable, necessary, and consistent with the situation. It may not extend to actions that are excessive or invasive.
Examples of Implied Consent
Implied consent is often applicable in various practical scenarios where individuals can reasonably assume that their actions or the circumstances imply their agreement or acceptance of a certain situation or action. Here are practical scenarios where implied consent commonly applies:
Routine Medical Procedures
- Vital Signs Monitoring: When a patient enters a healthcare facility, they may reasonably assume that healthcare providers will monitor their vital signs like blood pressure, pulse, or temperature as part of routine care.
- Blood Draws: In a healthcare setting, a patient extending their arm for a blood draw implies consent for the procedure, assuming they have not expressed objections.
Public Greetings and Interactions
- Handshakes: In many cultures, offering a handshake or accepting one is a customary way to greet and interact with others. The act of extending one’s hand implies consent to the handshake.
- Public Conversations: Engaging in a conversation with someone in a public space implies consent for that interaction unless the individual explicitly communicates their desire for privacy.
Online User Agreements and Cookies
- Website Browsing: When users visit a website, the use of cookies and data collection practices is often based on implied consent, provided the website displays a clear privacy policy and informs users of these practices.
- Acceptance of User Agreements: When users click “Accept” or “Agree” to terms and conditions or user agreements on websites or software, their actions imply consent to abide by those terms.
Security Measures
- Security Checks at Airports: Passengers going through airport security screening implicitly consent to security checks and screening procedures as a condition of boarding an aircraft.
- Bag Checks in Retail Stores: Shoppers in some retail stores may imply consent to bag checks upon exiting the store by shopping there.
First Aid in Emergency Situations
- Assistance in Emergencies: In cases of accidents or emergencies, individuals may assume implied consent for first aid and medical assistance when they are unable to give explicit consent due to their condition.
Common Courtesies
- Holding Doors Open: Holding a door open for someone implies consent for them to pass through.
- Sharing Public Spaces: Using public transportation, parks, and other public spaces implies consent to follow established rules and norms.
Observation and Recording
- Video Surveillance: In areas with visible security cameras, individuals may reasonably assume that they are being observed and recorded, implying consent to be monitored within the boundaries of legal requirements.
Social Media and Sharing
- Tagging in Photos: When someone tags another person in a photo on social media, it implies consent for the individual to be associated with the image.
- Sharing of Posts: Sharing someone else’s social media post typically implies consent for the sharing action.
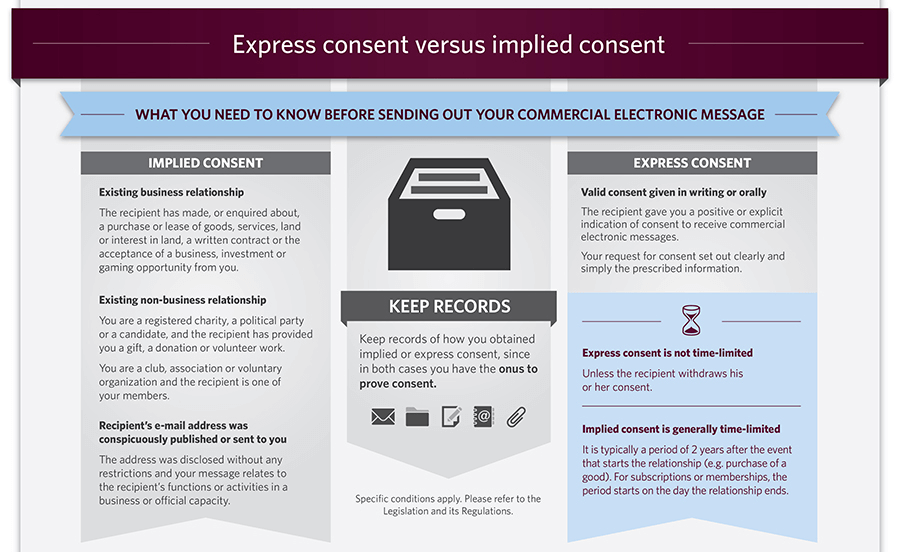
Comparison of Express and Implied Consent
When deciding which type of consent is most appropriate for your needs, it’s important to consider both the immediacy of the agreement required and the intensity of the undertaking. Express consent is more suitable for situations requiring direct authorization, while implied consent is often better suited for those involving less intrusive activities. Ultimately, there’s no single ‘correct’ choice – the type of consent you select should depend on the context and degree of formality present.
Express Consent: Meaning and Implications
Express consent is an unequivocal agreement that a person gives explicitly. This type of consent makes it clear to all parties involved that a person is intentionally agreeing to do something, such as sign a contract or grant permission for someone to use their image in a television commercial. It usually involves an explicit verbal or written statement, such as asking someone to sign their name on a document to confirm their agreement. Once given, express consent can be retracted under certain circumstances.
Implied Consent: Meaning and Implications
Implied consent is a more subtle concept than express consent. It refers to a situation where a person’s actions or behavior suggest they are compliant with a particular arrangement, but there may not be an explicit verbal or written statement confirming this. For example, if someone agrees to take part in an activity without voicing any objections, this could be viewed as implied consent. In contrast to express consent, implied consent is difficult to withdraw and tends to be presumed rather than actually given.
Consent in Healthcare
Consent is an essential factor in healthcare. It involves a patient giving permission for their medical information to be shared or used for certain purposes. There are two types of consent: expressed, which occurs when a patient has explicitly stated that they agree to something; and implied, where the patient has not expressly stated it but there is still evidence that they have given permission.

What is implied consent in healthcare?
Implied consent is particularly common when a patient is unable to communicate their wishes due to their age, mental state, or physical condition. For example, if they are unconscious or have an illness that prevents them from expressing themselves clearly. In such cases, doctors can still administer medical treatment based on assumed consent. Nevertheless, patients do have the right to withdraw implied consent should they have any doubts or concerns about data security.
It’s important to remember that informed consent is always paramount; while implied consent may offer a viable alternative, patients should also be aware of their rights and able to express them in order to ensure their safety and privacy.
When to Seek Express vs. Rely on Implied Consent
Expressed consent is a form of informed consent that involves the patient signing a document explicitly allowing for their participation in a study or treatment, and explicitly confirming their understanding of the terms and conditions of their agreement.
Implied consent, on the other hand, is based on a patient’s expressed consent given without needing to sign any documents; this can be verbal or nonverbal communication such as nodding or smiling during an explanation or conversation. Implied consent is often used on a daily basis in many healthcare settings, however, it is not sufficient for all types of medical situations such as:
- Whenever a child without the capacity to give legal consent or someone too ill to provide informed consent is involved, implied consent is not enough, and other measures must be taken.
- Implied consent does not apply to public health policies that are meant to benefit a greater population, as individuals cannot opt-out.
- Third-party information given by a patient to their doctor also requires more than just implied consent due to potential implications for the entire family.
- People competent to give consent may be unable to refuse due to duress or constraints, meaning their implied consent may not be considered valid or reliable.
In any of these cases, further steps must be taken to ensure that proper permissions are obtained before proceeding with treatment or operations. All states have different laws related to consent, while there are also federal guidelines issued by the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
Conclusion
Consent is a fundamental element of any healthy relationship or legal transaction. To ensure the autonomy and safety of all parties involved, understanding the nuances between express and implied consent is crucial. Express consent involves explicit verbal or written agreements whereas implied consent is inferred from a person’s behavior or circumstances. This distinction has special importance in healthcare, where informed consent should always be sought, either through explicit approval or in urgent situations where immediate action is necessary.
Furthermore, it’s also important to take further measures when dealing with minors or other individuals who are not able to give legal consent. By taking these precautions, we can ensure that all parties involved are well-informed and have equal rights to make their own decisions. Ultimately, respecting an individual’s right to consent is essential for maintaining the ethical and legal standards of our society. By keeping these principles in mind, we can foster strong and healthy relationships across all aspects of life.




