Zero-Tolerance Law – Underage Drunk Driving
Contents
The creation of zero-tolerance laws came in direct response to the issue of drinking and driving by underage drivers. Over time, statistics have shown an increase in alcohol-related accidents and deaths, with a great number of them occurring with minors. In the case of accidents among drivers under the age of 21, a large portion of deaths is related to illegal alcohol consumption. These zero-tolerance laws were established to target underage drinking and driving.
States with zero tolerance laws: Since 1988, all 50 states and DC have enacted zero-tolerance laws requiring drivers under the age of 21 to have a BAC of 0.02% or less. For the average person, the 0.02 limit is equivalent to about one drink.
The purpose of these laws is to deter people under the age of 21 from consuming alcoholic beverages and driving a vehicle. One law is broken already when they’ve consumed alcohol, but to get behind the wheel of a vehicle breaks another one, and poses many threats. When any driver consumes alcohol, their driving skills can become impaired making them more susceptible to an accident.
What does zero tolerance mean?
Imagine how much worse that can be for a young person who is still learning and developing driving skills, and possibly how more prone it can make them for the same. The key to zero tolerance laws was not only to stop underage drivers from drinking as far as law-breaking but also for the safety of themselves and everyone around them. The adoption of zero-tolerance laws has not been made by every state, but they still penalize minors who drink and drive more severely. The most commonly imposed zero tolerance BAC level by states for zero tolerance laws is 0.02, although they also use 0.00 and 0.01.
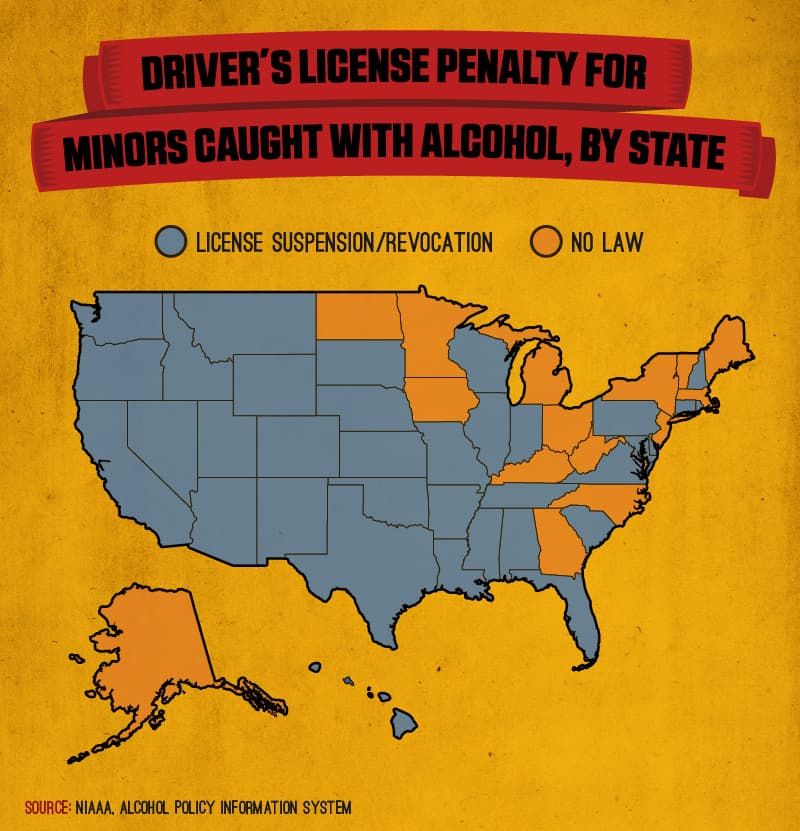
Penalties
Underage drinkers contribute to a disproportionate number of alcohol-related driving fatalities, so the standards and penalties for underage DUI convictions are much stricter than those for adults. Depending on the severity of the offense, penalties may include jail time, suspension of one’s driver’s license, hefty fines, mandatory alcohol education or rehabilitation programs, and community service. Moreover, some insurance companies may decide to terminate your policy after an underage DUI conviction, while most will increase the cost of monthly premiums for high-risk policies. It is therefore essential to be mindful of the serious consequences that can arise from an underage DUI conviction.
The penalties each state imposes for zero-tolerance law violators vary. Administrative penalties usually refer to the refusal to take a BAC test such as a breathalyzer, alcohol urine test, or blood alcohol test, or the results of them and can result in license suspension immediately. Criminal penalties will pertain once the conviction is made and can vary from penalties such as community service, large fines, alcohol-awareness programs, license suspension/revocation, etc.
- Fifteen states in the United States don’t have mandatory or discretionary laws that impose loss of driving privileges for minors convicted of alcohol possession.
- The most stringent possible penalty for minor offenders is found in Nevada where license revocation can last up to 730 days.
- Other states like California, Oregon, Utah, Tennessee, and Washington all impose mandatory bans of no less than 365 days.
- In Idaho, a similar ban lasts up to 365 days, with a maximum discretion of 365 days also seen in New Hampshire and South Dakota.
- Virginia enforces a 180 to 365-day license suspension depending on the age of the offender.
- The most lenient states restrict suspensions and revocations to no more than 30 days. These include Connecticut, Delaware, Kansas, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Rhode Island and Texas.
All of these laws impose varying degrees of disciplinary measures for minors caught in possession of alcohol –and are designed to ensure safety on our roads while still conveying the gravity of the offense.
DUI Minors
Also, if the person is additionally under 18 years of age making them a minor, they will experience even stiffer penalties including most likely jail time in addition to license suspension and community service. Due to the seriousness that the states take towards DUI and underage drinking as separate issues when they are combined, they look down upon the charges greatly. A person found to be in direct offense of the zero tolerance law should not expect to receive any sort of leniency from a judge or prosecutor. It is a matter that is taken with high regard, and extremely seriously.
Since establishing zero tolerance laws, many states have seen a slow but steady change in lowering the number of underage drunk drivers on the roadways. They have also deterred people under the age of 21 from drinking alcohol regardless since they know they may need to drive somewhere, and don’t want to risk the consequences. The logic is, the stricter the penalty is for breaking a law, the fewer people you will have breaking that law.
Background
Zero-tolerance laws were put into effect to try to deter the number of underage drunk drivers. These laws are adopted by some states and imply certain penalties for people caught driving legally intoxicated, that are under the age of 21.
These drivers are not subject to the standard 0.08 Blood Alcohol Content level that exists in all states, but rather a much lower one that varies. Most states use 0.02 as their zero tolerance BAC level, while others fluctuate between 0.00 and 0.01. These zero-tolerance laws carry more severe penalties than the normal DUI laws and can be argued less in court primarily due to their nature.
Creation and Purpose
The rise in alcohol-related deaths and accidents led to a push for stricter DUI laws. But when a large number of these deaths proved to be from underage drinkers, a new focus was made. This focus was placed precisely on underage drinking followed by driving, which called for a new set of laws to be made. These laws were known as zero-tolerance laws.
They are designed to lower the number of drunk drivers by imposing a low BAC level, and stiff penalties for those in violation of them. In essence, they are also aimed at deterring people under the age of 21 from consuming alcoholic beverages altogether. This would be due to the fact that most teenagers drive constantly, fear of consequences would keep them from drinking.
State Mandates
Most of the states that have zero tolerance laws have parts of these laws that pertain to other areas. These areas can include drugs and firearms. These zero-tolerance laws are used mainly by schools, to show discipline and lack of leniency to the student body for improper behavior.
State mandates exist that are set provisions that guide the educational institution in the proper dealing of those found in violation of zero tolerance laws. The universal treatment of anyone violating these laws can help portray the seriousness of the offenses. State mandates have been protested by parents and school officials alike, due to their said lack of focus on individual matters.
Statistics
The addition of zero tolerance laws by certain states was done in direct response to statistics dealing with alcohol-related accidents and deaths by underage (< 21 year-olds) drivers. Now, after their years of existence and strict enforcement, statistics have gone to help show the positive effect that zero-tolerance laws have had on the population.
The slight but decreased number of alcohol-related accidents due to underage drinking and driving is a clear sign of that. Of course, there are still cases where these accidents and deaths occur, but if the numbers are slowly diminishing, perhaps a steady decrease will be imminent. This is if these laws continue to serve their purpose along with other underage drunk driving countermeasures.
Texas Zero-Tolerance Law
The ZERO TOLERANCE law in Texas makes it a crime for any minor to operate a motor vehicle, including a watercraft, in a public area while having ANY detectable level of alcohol in their system. Driving Under the Influence of Alcohol by a Minor is a felony (DUIA by a Minor).




